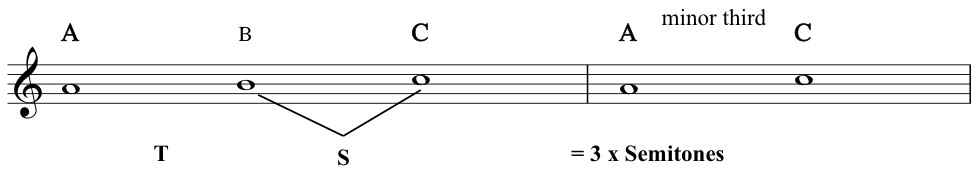Prologue
Last December (2019), I received an email about a survey from Coursera. After filling it out, I was given the chance to take a course from Coursera for free. The options were limited to entry level lessons from a variety of fields, from which I picked The Fundamentals of Music Theory offered by The University of Edinburgh.
Notes for Week 1
Musical Notes
Early in the history, there was not a universal form for representing musical notes, nor was there audio recorder, so keeping record of a piece of melody became problematic, especially when the aim was to pass it on. The
stave (staff)with musical notes was hence eventually formed to represent melodies in a standardized way.The lines on a stave are called
ledger lines.There are seven alphabetical
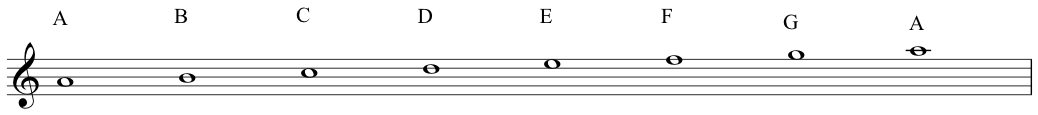
notenames in ascending (⬆️) order:A(La)B(Ti)C(Do)D(Re)E(Mi)F(Fa)G(So)![Seven notes up the stave]()
Notes on a keyboard (commonly piano):
![Notes on a keyboard]()
When necessary, additional line segments can be used to supplement (extend the range of) ledger lines so as to mark higher (lower) notes.
The four ascending (⬆️) notes that fall prespectively in the four spaces in the standard 5-line stave are
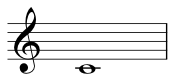
F-A-C-E, “face”.Middle C: the lowerCwith one ledger line segment below the stave, normally at the middle (center) of a keyboard:![Middle C]()
Octaves
The inteval between two alphabetically adjacent musical notes is called a
second.- Similarly, there are
third,fourth,fifth, up toseventh.![A second to A sixth]()
- Similarly, there are
When the interval reaches 8, it becomes an
octave![An octave]()
Tones and Semitones
(Refer to a keyboard)
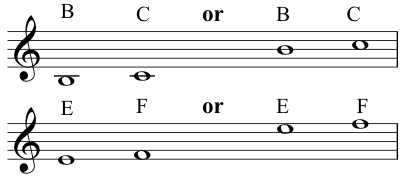
Tone: the distance of a second that has a black key in the middleSemitone: the distance of a second that does not have a black key in the middle- There are only two sets of semitones: between
BandC, and betweenEandF![<code>B-C</code> and <code>E-F</code> semitones]()
- There are only two sets of semitones: between
Scales
Diatonic mode: natual octave scales- “When the pattern of tones and semitones is different, the scale sounds different - formally it has a different quality.”
- The seven diatonic modes
CIonian (same as C major): TTSTTTSDDorian: TSTTTSTEPhrygian: STTTSTTFLydian: TTTSTTSGMixolydian: TTSTTSTAAeolian (same as A natural minor): TSTTSTTBLocrian
- “Music doesn’t always start on its tonic, but it often finishes on it, … should feel like home.”
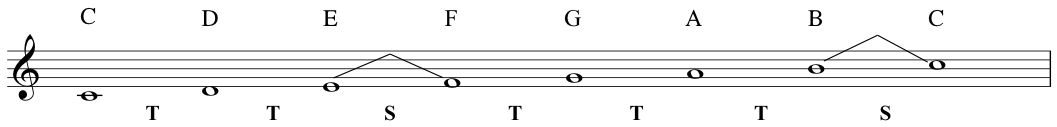
The C Major Scale
Cis the tonic- Diatonic scale: a scale that has a pattern of 2 semitones and 5 tones within an octave
![The C major scale]()
- Some C major songs:
- Twinkle Twinkle Little Star
- Frere Jacques (Brother John or Are You Sleeping)
- Mary Had a Little Lamb
Chords
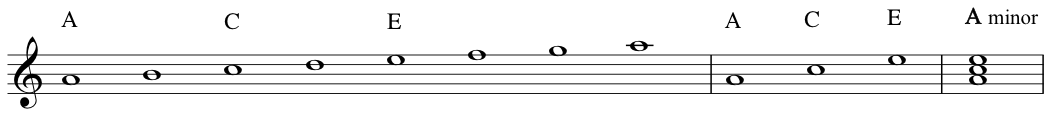
A
chord: Music notes played simultaneously to harmonize melodyTriad (chords): a three-note chord consisting of 2 thirds- Represented as three notes stacked
C major triad is the
tonicof the C major scale.![C major triad]()
A minor triad is the
tonicof the A minor scale.![A natural minor triad]()
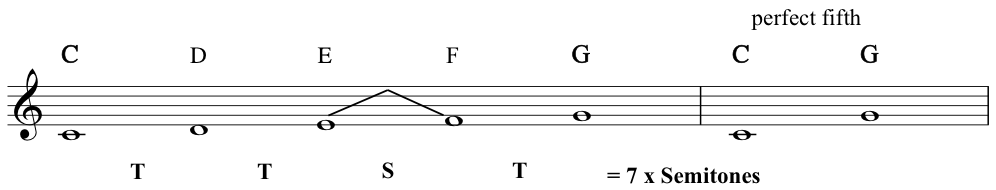
Perfect fifth: a fifth containing 7 semitones (a tone is counted as two semitones)![Example perfect fifth]()
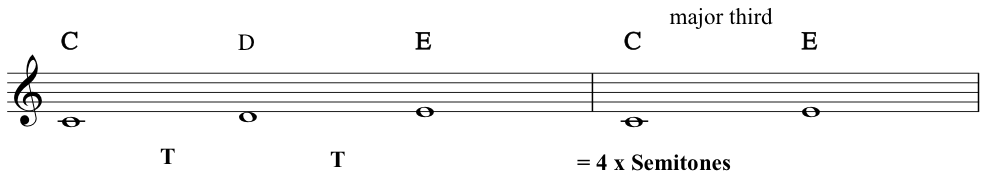
Major third: a third containing 4 semitones![Example major third]()
Minor third: a third containing 3 semitones![Example minor third]()
A
perfect fifthis:- A
major chordif starting with a major third - A
minor chordif starting with a minor third
- A
7 natural triads: 3 major chords, 3 minor chords, and a
diminished chordCmaj,Fmaj, andGmajDmin,Emin, andAminBdim(diminished, as having an imperfect fifth)![natural triads]()
The 3 primary chords
Tonic triad: triad built on thetonic(starting note) of a scaleSubdominant triad: triad built on the fourth note of a scaleDominant triad: triad built on the fifth note of a scale- For C major scale:
Cmajis the tonic triad,Fmajis the subdominant triad, andGmajis the dominant triad respectively![Tonic, subdominant, and dominant triads for C major scale]()
- For C major scale:
- Harmonization using natural (primary) triad chords
![Harmonization using primary chords]()